Boron Nitride Ceramic(BN)
 Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramics : Properties, Types, and Applications Explained
Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramics : Properties, Types, and Applications Explained
Boron Nitride (BN) is a compound composed of equal parts of nitrogen (N) and boron (B), with the chemical formula BN. Based on its crystal structure, BN is classified into four forms: hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), cubic boron nitride (c-BN), rhombohedral boron nitride (r-BN), wurtzite boron nitride (w-BN) , Pyrolytic boron nitride (PBN) and Conductive Boron Nitride(TiB2-BN). This discussion primarily focuses on hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) and Conductive Boron Nitride(TiB2-BN) while the other three types are briefly introduced.
This image shows the crystal structures of the four main forms of boron nitride (BN).
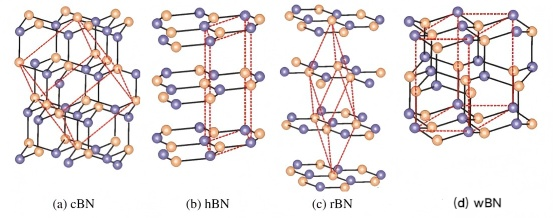
Image Source: “Bemerkungen über die Bildung von Verbindungen des Bors und Siliciums mit Stickstoff und gewissen Metallen” by W. H. Balmain.
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN): The “White Graphite”
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), also called α-BN or graphitic BN (g-BN), is structurally similar to graphite but appears as an ivory-white material, earning it the nickname “white graphite.” It is a key engineering ceramic with unique characteristics:

(a) Graphite structure; (b) h-BN structure; (c) Top view of graphite; (d) Top view of h-BN.
Key Properties of Boron Nitride h-BN
- Crystal Structure: h-BN features a layered structure with boron and nitrogen atoms alternately arranged in hexagonal patterns through sp² hybridization. These layers stack along the C-axis in an ABAB pattern, with strong covalent bonds within layers and weaker van der Waals forces between them.
- Performance: It offers self-lubrication, excellent electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, resistance to chemical corrosion, and ease of machining.
Boron Nitride Ceramic (b-BN)property chart
| Product Model | W-BN-H | W-BN-99 | W-BN-A | W-BN-B | W-BN-C | W-BN-D | W-BN-E | W-BN-S |
| Composition | BN > 99.7% | BN > 99% | BN + Al + Si | BN + Zr + Al | BN + SiC | BN + ZrO2 | BN + AlN | BN + SiN |
| Color | White | White | White | White | Greyish-Green | White | Greyish-Green | Dark Gray |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.50 – 1.60 | 1.95 – 2.05 | 2.20 – 2.30 | 2.25 – 2.35 | 2.40 – 2.50 | 2.75 – 2.85 | 2.75 – 2.85 | 2.20 – 2.30 |
| Electrical Resistivity (Ω·cm) | > 10¹⁴ | > 10¹⁴ | > 10¹³ | > 10¹² | > 10¹² | > 10¹³ | > 10¹³ | > 10¹³ |
| Max.Using Temp In Air(℃) | 900 | 900 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Max.Using Temp In Inert(℃) | 2100 | 2100 | 2000 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 |
| Max.Using Temp In Vacuum(℃) | 1900 | 1900 | 1750 | 1500 | 1500 | 1800 | 1500 | 1800 |
| Bending Strength (Mpa) | 18 | 30 | 60 | 85 | 85 | 100 | 120 | 220 |
| Compressive Strength (Mpa) | 25 | 45 | 145 | 145 | 150 | 220 | 220 | 400 |
| Thermal Expansion (25°C – 1000°C) (10^-6/K) | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2 | 2 | 2.8 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 35 | 40 | 35 | 30 | 30 | 45 | 35 | 55 |
| Hardness HSD | 12 | 18 | 40 | 45 | 45 | 40 | 40 | 45 |
| Applications | high-temperature Vacuum | high-temperature Vacuum | Powder Metallurgy | Powder Metallurgy | Powder Metallurgy | Metal Casting | Powder Metallurgy | Powder Metallurgy |
| Insulators for High Temperature Furnace | √ | √ | ||||||
| Crucibles for Metal Evaporation | √ | √ | ||||||
| Parts for Melting Metals or Glass | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Casting Molds for Metal or Alloy | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| High Temperature Support Parts | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Transport Pipes or Nozzles for Melting Metal | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
*The values represent typical material properties and may vary depending on product configuration and the manufacturing process,
For further information, do not hesitate to contact us.
Three types of Boron Nitride ceramic material:
Boron Nitride h-BN
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN)

Conductive Boron Nitride (TiB2-BN)
Pyrolytic boron nitride (PBN), also known as chemical vapor-deposited boron nitride (CVD-BN), is a high-purity form of boron nitride produced through chemical vapor deposition (CVD). This process involves the high-temperature pyrolysis of boron halides and ammonia in a vacuum environment.
Property of PBN Ceramics
| property | Unit | Value |
| Density | g/cm³ | 2.1 |
| Total Metal Impurities | ppm | ≤10 |
| melting point | ℃ | Non |
| Electrical Resistivity | Ω.cm | 1014-1015 |
| CTE (oefficient of Thermal Expansion) | μm/m·K | 2 |
| Dielectric Strength | Kv/mm | 55 |
| Thermal conductivity(1000℃) | w/mk | 51 |
| Hardness | Mohs | 4 |
| flexural strength | Mpa | 240 |
| Yield Strength | Mpa | 81 |
While PBN shares similarities with hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), it also contains a certain degree of turbostratic structure. One of its key advantages is its exceptionally high purity, reaching 99.99% or higher.
Unlike conventional hot-pressed boron nitride (BN), PBN does not require sintering or the addition of binders. Instead, it is directly deposited into thin sheets or formed into complex shapes such as PBN tubes, PBN rings, and PBN thin-walled containers(PNB Crucible).
How to Make Boron Nitride Ceramic Conductive?
Conductive Boron Nitride (TiB2-BN) also known as Black Boron Nitride, is a composite material made by adding conductive fillers, such as TiB2, to traditional boron nitride materials (usually hexagonal boron nitride, h-BN). Since boron nitride itself is an insulating material, this composite form of boron nitride (h-BN) combines the excellent properties of boron nitride (such as high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and superior lubricity) with electrical conductivity.
Contact Us for Custom Solutions!
We specialize in providing high-performance boron nitride ceramic products tailored to your specific applications. Whether you need PBN crucibles for GaN crystal growth or boron nitride crucibles with non-uniform wall thickness produced by the CVD process, we offer customized solutions to meet your requirements. Additionally, we supply BN Flow Control Nozzles, boron nitride setter plates, saggers, and push plates for high-temperature applications.