Overview of Advanced Ceramic Materials (2025)
Advanced ceramics, also known as fine ceramics, technical ceramics, or precision ceramics, is a special category of industrial ceramics.
These materials are composed of high-purity inorganic non-metallic compounds, which can be naturally occurring or artificially synthesized. They are processed into polycrystalline solids through precision molding and high-temperature sintering techniques.
To obtain specific properties or unique functions, advanced ceramics require strict control of chemical composition, the use of rigorous molding processes, and fine-tuning of their microstructure at high sintering temperatures.
Due to their superior performance, advanced ceramics are widely used in aerospace equipment, laser systems, electronic devices, military applications, traditional energy systems, renewable energy technologies, fluid control systems, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
Advanced Ceramics Comprehensive Guide: Classification and Applications of Structural and Functional Ceramics

Advanced ceramics categories: chemical composition classification (oxides, nitrides, carbides, borides)
| Advanced ceramics category | Major advanced ceramic materials |
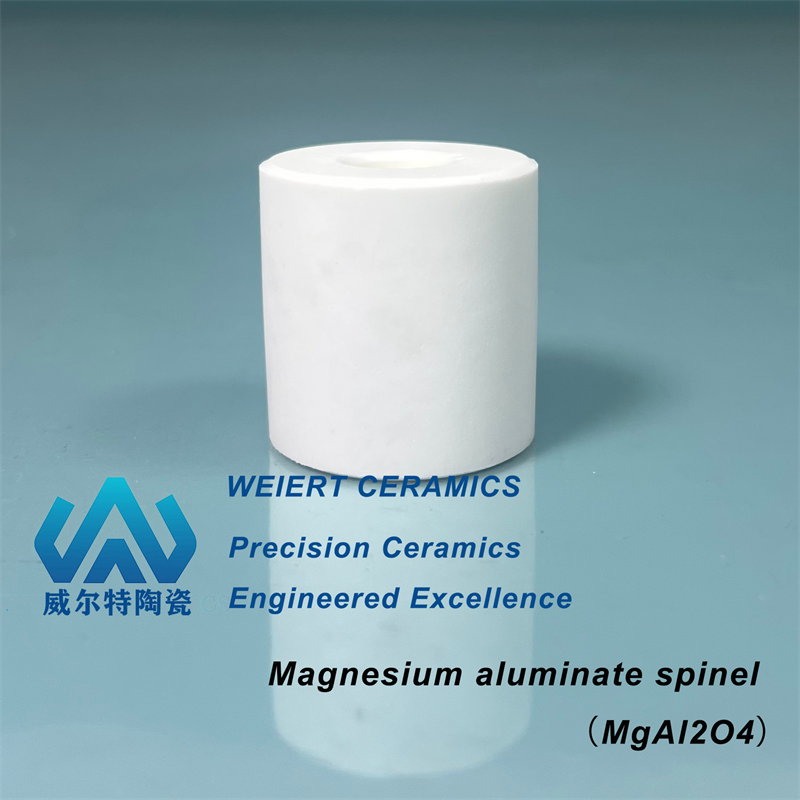
| oxides | Al2O3、SiO2、MgO、BeO、ZrO2、TiO2、V2O5、MgAl2O4、3Al2O3·2SiO2、BaTiO3、CaTiO3、PZT、PbTiO3 |
| carbide | Silicon carbide, titanium carbide, tungsten carbide, boron carbide |
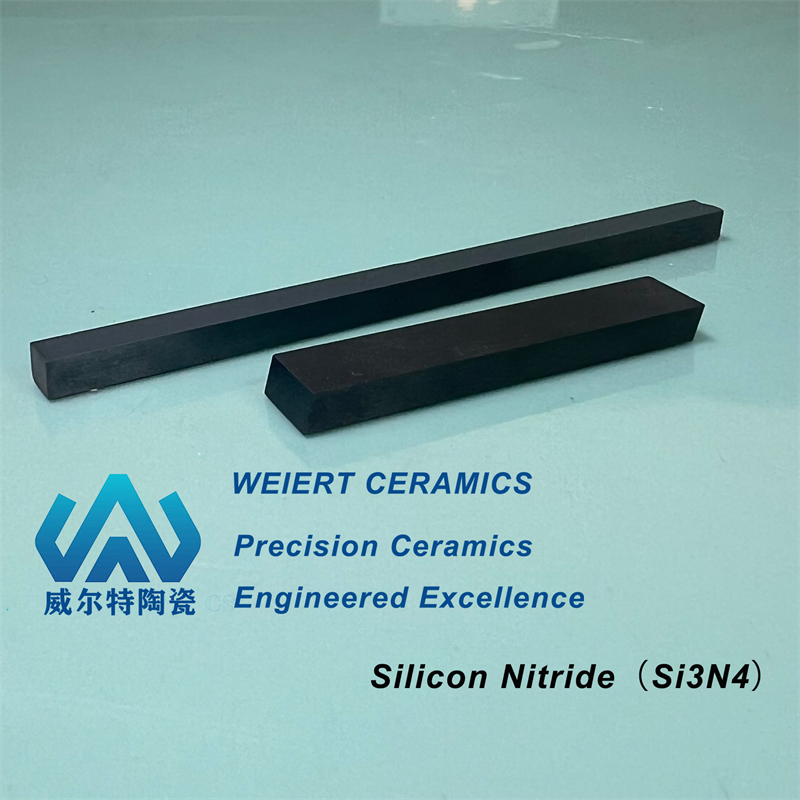
| Nitrogen compounds | Si₃N₄、TiN、BN、AlN、C₃N₄ |
| Borides | TiB₂,ZrB₂ |
Trusted Advanced Ceramics Manufacturer
WEIERT CERAMICS is a manufacturer specializing in innovation and production of advanced ceramics, not a trading company. Guided by the philosophy of Kazuo Inamori, we integrate his principles into our business management and manufacturing practices. We are committed to optimizing management processes and driving technological innovation to provide advanced ceramic products that meet customer expectations in quality while remaining competitively priced.

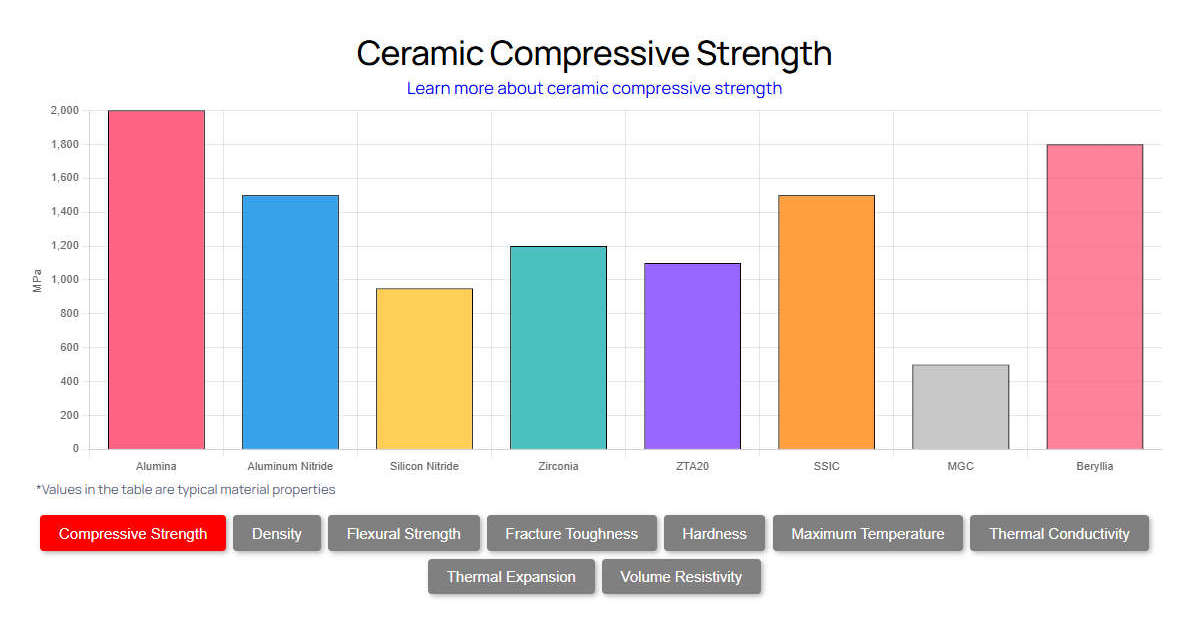
Ceramic Strength & Durability
Focusing on compressive strength, toughness, and wear resistance to ensure reliable performance.

Ceramic Thermal Performance
Emphasizing thermal conductivity, expansion, and stability to optimize heat management.

Ceramic Electrical Properties
Considering insulation, conductivity, and dielectric strength for efficient functionality.
Ceramic Chemical Resistance
Focusing on corrosion resistance and stability to protect against chemical degradation.